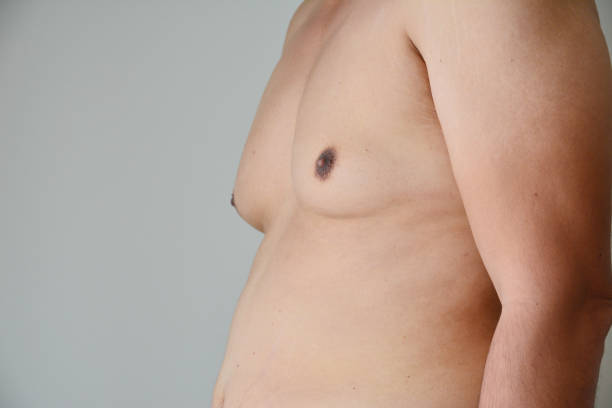
Gynecomastia is the clinical term for the condition that causes male breast tissue to grow, which is normally a combination of glandular tissue and breast fat. Gynecomastia symptoms will vary; however, the main concern for many men considering gynecomastia surgery is the appearance of puffy nipples and “man boobs”. Although stripping fat and building lean muscle may help reduce the appearance of man boobs, there are only two options when excess growth of glandular tissue is causing the appearance of man boobs: medication and surgery.
Gynecomastia Diagnosis
Assessment of gynecomastia can be done during a physical examination. Before surgery, a range of general blood tests will be performed. The most common diagnostic tool is breast ultrasonography (USG); this is usually only required if there are any concerns following a physical examination.
Grades of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia symptoms are categorised into four grades:
1. Mild, with slight growth of glandular tissue and/or puffy nipples (most likely to respondto medication)
2. Mild to moderate breast tissue growth, with a noticeable feminine breast shape
3. Moderate to significant breast tissue, with a very feminine breast shape and excess skin
4. Significant glandular tissue growth and breast fat, with considerable excess skin and asevere breast crease.
Medication for Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia Surgery is the fastest and most reliable solution for gynecomastia symptoms and, unlike medication, does not have long-term side effects. With that in mind, medication can cause a degree of regression of glandular tissue and reduce symptoms such as tenderness and puffy nipples. For some men, medication-induced reduction in the appearance of “man boobs” is sufficient, and surgery is not required. The main issue, apart from side effects, is that when medication is stopped, gynecomastia symptoms may return.
Currently, there are no prescription drugs approved by the FDA to treat gynecomastia symptoms. FDA-approved drugs can be prescribed as “off label”, meaning they have not been approved to treat the medical condition they are being prescribed for, in this case, gynecomastia. The most common FDA-approved drugs prescribed “off label” for gynecomastia include:
Tamoxifen is a type of selective oestrogen receptor modulator (SERM) “off-label” medication used to treat gynecomastia symptoms that comes in tablet and liquid form. FDA approved for the treatment of breast cancer in both men and women, the effect of Tamoxifen has been assessed in clinical studies for the treatment of gynecomastia symptoms and reduction of glandular tissue. The results of trials indicate treatment with Tamoxifen may be effective for some men in partially reducing the size of male breast tissue and reducing other gynecomastia symptoms.
- Clomiphene (CLOMID)
Another type of anti-estrogen drug often referred to as an “estrogen blocker” is Clomiphene. Used for years by bodybuilders, Clomiphene is the most common anti-estrogen drug prescribed “off-label” to treat gynecomastia. The results demonstrated in clinical trials are limited to treatment during puberty.
- Anastrozole (Arimidex®)
Anastrozole is a type of aromatase inhibitor that is often used for the treatment ofGynecomastia, for men taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and older menwith low testosterone levels. They work by increasing testosterone levels, and although improvements in gynecomastia symptoms have been reported, in clinical trials the results were comparable to the placebo group.
Non-FDA-approved Drugs or Supplements
There are a variety of gynecomastia supplements; a few of the ones used and discussed by men in gynecomastia forums are GyneMax, Gynexin and Gynectrol. These non-prescription pills for gynecomastia are “fat burners”, which, in men who have pseudo gynecomastia, may help reduce fat tissue and the appearance of male breasts, “man boobs”. None of these pills affect hormonal balance and can not reduce breast glandular tissue.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Gynecomastia
Non-surgical treatments for gynecomastia include cool sculpting and warm sculpting, often referred to as fat-melting. It is important to note that this type of gynecomastia non-surgical treatment only reduces breast fat and will not reduce glandular tissue, which is the true cause of gynecomastia. However, when mild to moderate gynecomastia symptoms appear worse due to breast fat, removing fat tissue will reduce overall breast size.
Gynecomastia Surgery and Anaesthetic Options
Modern gynecomastia surgery offers a range of surgical techniques using small incisions made around the edge of the areola, which, once healed, are normally difficult to detect. Most procedures can be performed under a local or a general anaesthetic.
Grade 1
Liposuction may be sufficient in cases with very little excess glandular tissue. This can be performed under a local anesthetic.
Grade 1 and 2
The “pull-through technique” is a surgical technique that only requires a small 5mm incision. The incision is made at the lower edge of the areola. Glandular tissue is excised through the incision, and liposuction sculpts the surrounding tissue and removes excess breast fat. The stitches are dissolvable, and once healed, the scar is difficult to detect, making this the procedure of choice for grade 1 and some cases of grade 2 gynecomastia. This procedure is normally performed under local anaesthetic, although some plastic surgeons may recommend a general anaesthetic.
Grade 2 and 3
When the “pull-through technique” is not appropriate, the most common surgical method uses the Webster method, with a peri-areolar or trans-areolar incision around the bottom curve of the areola. The scar is concealed by the pigmentation difference between the areola and the chest skin. This method does not allow for skin resection. It is only suitable for men with good skin thickness and elasticity to prevent lax skin following the removal of glandular tissue and fat. Generally, this procedure is performed under a general anaesthetic; however, some plastic surgeons may also offer this under a local anaesthetic.
Grade 3 and 4
When grade 3 gynecomastia occurs, there will be a requirement for skin resection; this will normally involve scars that extend across the chest. Another option, suitable for minimal to moderate skin laxity, is a two-stage procedure. The first procedure uses the Webster Method and is followed by a second procedure approximately four to six months later. The second procedure involves skin resection with a peri-areola lift; this only requires an incision around the edge of the areola, which is well concealed when healed. This procedure is usually performed under a local anaesthetic.
Grade 4
A double mastectomy is the most appropriate surgical procedure for grade 4 gynecomastia. It may also be the preferred option by men with grade 3 gynecomastia who have thin or lax skin or want a surgical procedure. The procedure involves an incision under the breast fold, leaving a scar across the chest close to the armpit. The benefit of this procedure is the facilitation of adequate skin resection for a male contoured chest, eliminating loose skin or ripples. The nipple-areola, which is often abnormally large, is also made smaller. This procedure is almost always performed under a general anaesthetic.
“The difficulty faced by a surgeon performing a double incision mastectomy is the removal of the nipple-areola complex (NAC). Not only is it vital that the tissue is kept healthy and blood vessels are reattached to prevent necrosis (death of tissue) following the procedure, the position of the NAC is critical to creating a tightly contoured masculine chest that is aesthetically correct. The main concerns with a mastectomy are the size of the scars and a reduced lack of sensation in the nipple. In my experience as a plastic surgeon who specialises in gynecomastia surgery, patients are extremely happy with the outcome.” Dr. Miguel Delgado, M.D
Gynecomastia Compression Garments Post Op
Following gynecomastia surgery, a compression vest will be put on. This needs to be worn 24/7 and should only be taken off for short periods when showering. On average, the vest is worn for between four to six weeks.
Gynecomastia Surgery Complications
Complications are less likely when surgery is performed by an experienced plastic surgeon in an appropriate surgical suite or theatre.
The main complications are:
- Hematomas and seromas, which can both be avoided by drains or, if needed, can be resolved with drains.
- Infection, although the possibility of infection is significantly reduced when surgery is performed in hygienic facilities with sterilised equipment and antibiotics are prescribed following surgery.
Additional complications include:
- Numbness around nipple due to nerve damage
- Necrosis (death of tissue)
- Scarring
- Unsatisfactory results, normally when additional skin resection is required.
Q & A With Dr. Miguel Delgado, M.D.
Dr. Miguel Delgado, M.D. is a world-renowned Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon, a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, and a recognized expert in the field of gynecomastia surgical procedures.
Why do you recommend a general anaesthetic for certain procedures instead of a local anaesthetic with twilight (IV) sedation?
“This is an excellent question and is surgeon-specific. I use general anesthesia for 95% of my primary gynecomastia cases and most revision gynecomastia cases. Forty-five percent of my patients are gynecomastia revisions and are unhappy with other practices’ outcomes.
I use general anesthesia to have complete control of the surgical environment. This allows the patient to be completely comfortable to be aggressive with my techniques. This surgery is performed through a one-inch incision using a lighted retractor, so any bleeding makes it difficult. When someone is awake, this can be a real challenge.
However, some surgeons promote local anesthesia and are competent in performing surgery in the environment.”
Do patients ever need to stay in hospital overnight?
“Patients never need to stay overnight for gynecomastia surgery. It is an outpatient procedure.”
How often are men with grade 1 gynecomastia satisfied following liposuction as a stand-alone procedure?
“This is another excellent question that defines gynecomastia and how best it can be treated for a cure. The definition of gynecomastia is breast development in a male’s chest. Breast tissue can not be liposuctioned away, but the fat can. When a patient with gynecomastia grade 1 undergoes liposuction only, it can look worse by leaving behind a ball of breast gland that looks more discrete and obvious. Liposuction is the number one reason for revision surgery in my practice.”
Are there any specific qualifications or professional bodies patients in the USA should check the plastic surgeon has passed or belongs to?
“Yes, this is very important. The physician should be a plastic surgeon board certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery. This board certification is the goal standard in the United States. This is intense oral and clinical testing that occurs after plastic surgery training that takes several years. In addition, becoming a member of the American Society of Plastic surgery and a bonus would be a member of the American Society of Aesthetic Surgery. These are the most important professional bodies which are essential to belong to.” Dr. Miguel Delgado, M.D.